Difference between revisions of "Modular Ring Imaging Cherenkov Detector (mRICH)"
(→Second mRICH Prototype Beam Test) |
|||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The goal of the modular aerogel RICH (mRICH) is to provide hadronic PID capability with momentum coverage from 3 to 10 GeV/c with a compact design in order to overcome the space limitations of the EIC experiments. Although the multi-layer proximity-focusing RICH design, such as ARICH at BELLE2, can achieve three-sigma K/π separation at 4 GeV/c, a larger expansion volume is required for PID in higher momentum range. | The goal of the modular aerogel RICH (mRICH) is to provide hadronic PID capability with momentum coverage from 3 to 10 GeV/c with a compact design in order to overcome the space limitations of the EIC experiments. Although the multi-layer proximity-focusing RICH design, such as ARICH at BELLE2, can achieve three-sigma K/π separation at 4 GeV/c, a larger expansion volume is required for PID in higher momentum range. | ||
| − | A multi-layer proximity-focusing RICH design increases PID separation power by increasing number of detected photons (Nγ) by adding successive layers of radiator while keeping the uncertainty of Cherenkov angle (σ_θ) of single photon measurement. In contrast, the novel lens-based mRICH design improves the separation power by minimizing the uncertainty σ_θ as a result of lens focusing, | + | A multi-layer proximity-focusing RICH design increases PID separation power by increasing number of detected photons (Nγ) by adding successive layers of radiator while keeping the uncertainty of Cherenkov angle (σ_θ) of single photon measurement. In contrast, the novel lens-based mRICH design improves the separation power by minimizing the uncertainty σ_θ as a result of lens focusing, and requires a smaller coverage of the photosensor plane. |
=Detector Design= | =Detector Design= | ||
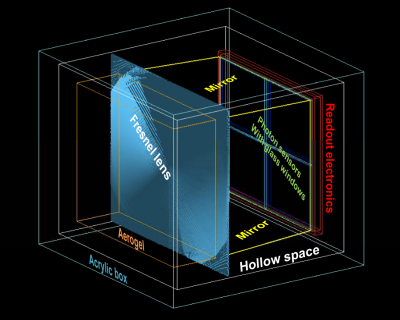
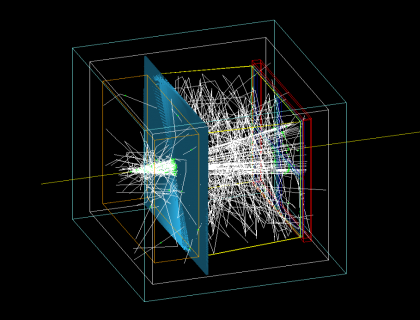
| + | Modular RICH detector consist of a block of aerogel as a radiator, a Fresnel lens, a set of four-sided mirror, and a sensor plane. When charged particle passes through the aerogel, it will emit Cherenkov photons in a cone shape. These Cherenkov photons will be focused by the Fresnel lens on the sensor plane, and form a shape ring image. | ||
{| | {| | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
| Figure 1.1 (b). Single 9 GeV/c pion simulation | | Figure 1.1 (b). Single 9 GeV/c pion simulation | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
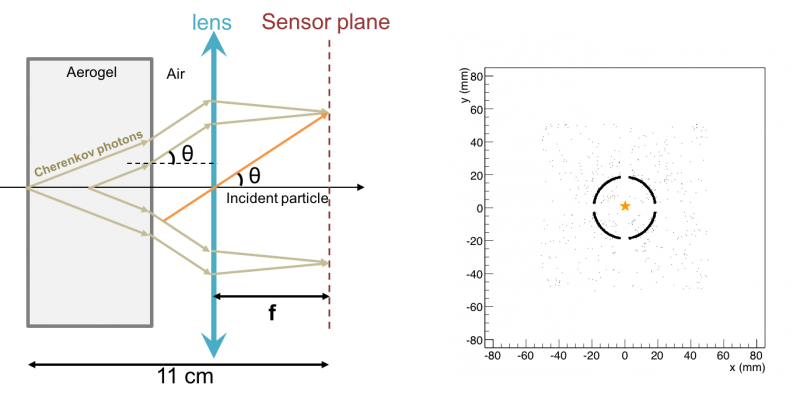
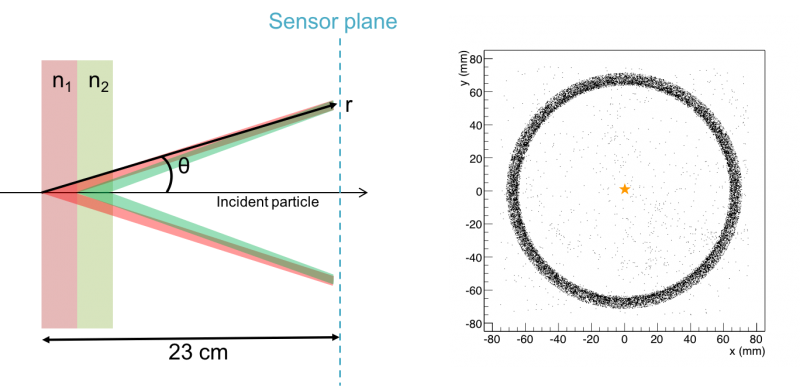
| + | There are two advantages of the lens-based design. Firstly, the ring image is smaller and thinner because of the focusing of lens (see figure 1.2 and 1.3). Secondly, in the case that charged particle travelling parallel but off the longitudinal axis (that is, the optical principal of lens), ring image will be shifted to the central area of the sensor plane (see figure 1.4 and 1.5). Therefore, the lens-based design enhances detector PID performance, while lowers the required sensor plane area per ring. | ||
{| | {| | ||
| Line 34: | Line 37: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Figure 1.5. Cherenkov ring image from particles that are incident at the third quadrant of the detector. | | Figure 1.5. Cherenkov ring image from particles that are incident at the third quadrant of the detector. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
=Fisrt Prototype and Beam Test= | =Fisrt Prototype and Beam Test= | ||
| + | '''First Prototype''' | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 73: | Line 70: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | Beam test set up at Fermilab Test Beam Mtest Facility for the first modular RICH prototype detector is shown in the picture below. The detector (black box) sit at the center of a aluminium frame. On both ends of the aluminium frame are hodoscopes. Each hodoscopes consist of four horizon finger-size ( | + | '''First Beam Test''' |
| + | |||
| + | Beam test set up at Fermilab Test Beam Mtest Facility for the first modular RICH prototype detector is shown in the picture below. The detector (black box) sit at the center of a aluminium frame. On both ends of the aluminium frame are hodoscopes. Each hodoscopes consist of four horizon finger-size (1cm x 1cm) scintillators, and four vertical finger-size scintillators. On the far right of the aluminium frame was trigger paddle. The beam was coming from right to left of the picture. | ||
{| | {| | ||
| Line 95: | Line 94: | ||
=Second Prototype= | =Second Prototype= | ||
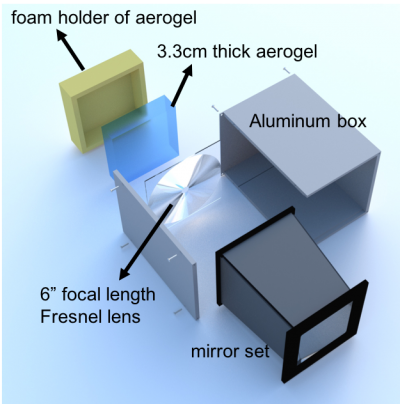
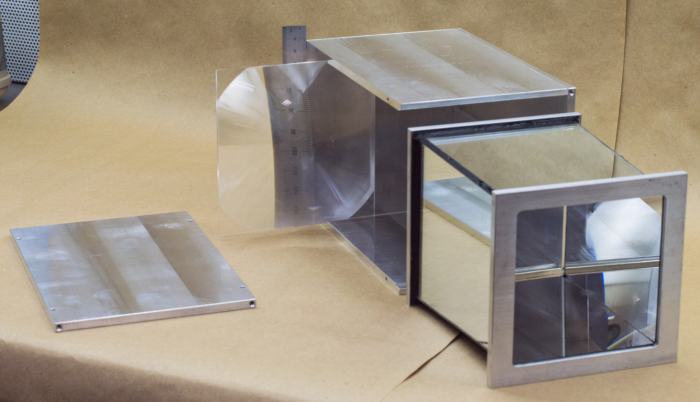
| + | '''Optimized Detector Design''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to enhance detector PID performance, the next mRICH prototype will use a longer focal length (6") Fresnel lens, and smaller pixel size (3mm × 3mm) photon sensors. Furthermore, the readout electronics will be separated from the optical components to avoid overheating. | ||
{| | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[image:Prototype2drawing.png|400px]] [[image:Prototype2pic.png|700px]] | | [[image:Prototype2drawing.png|400px]] [[image:Prototype2pic.png|700px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Figure 3. | + | | Figure 3.1. (left) 3D drawing of the second mRICH prototype. (right) construction of the second mRICH prototype. |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 122: | Line 124: | ||
| HAMAMATSU 13700 PMT array. Pixel size=3×3mm | | HAMAMATSU 13700 PMT array. Pixel size=3×3mm | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Projected Detector Performance of Next mRICH Prototype''' | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[image:Num sigma 6inFocalLength.png|500px]][[image:MRICH e pi separation.png|450px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
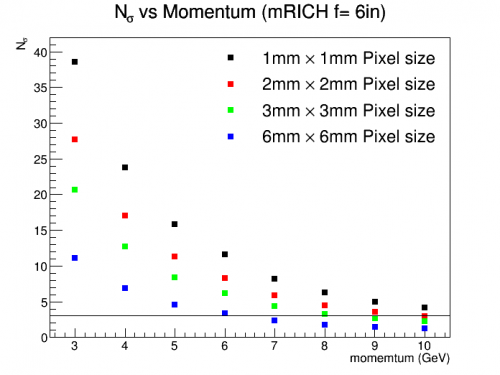
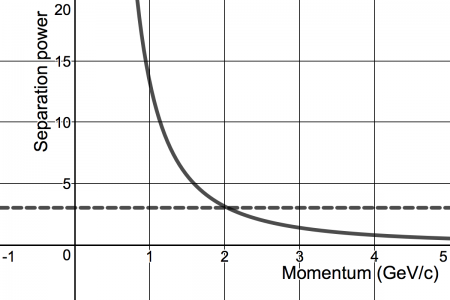
| + | | Figure 3.2. (Right) Projected K/pi separation power of modular RICH detector obtained from simulation using 6" focal length Fresnel lens with different pixel size photon sensors. K/pi separation power of second mRICH prototype is shown in green dots. (Left) Projected e/pi separation power of second modular RICH prototype. These plots indicates that with the second prototype design, the mRICH prototype can acheive 3-sigma of K/pi separation and e/pi separation up to 8 GeV/c and 2 GeV/c, respectively. | ||
|} | |} | ||
=mRICH Detector System Simulation= | =mRICH Detector System Simulation= | ||
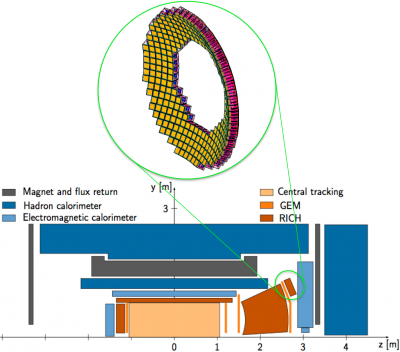
| − | *sPHENIX/ePHENIX | + | *mRICH detector system in sPHENIX/ePHENIX. The detector system which contains 284 modules of mRICH, covers 1.0 to 2.0 rapidity. |
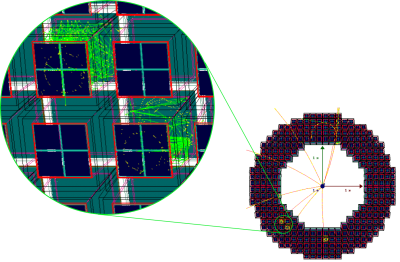
| − | *JLEIC | + | *:[[image: MRICH in ePHENIX.png |center|400px|mRICH in ePHENIX]] |
| + | *:Event display of 10 negative pion tracks (view from down stream) from simulation. An enlarged view is shown on the left. | ||
| + | *:[[image: MRICHsystem ePHENIX.png|center|400px|mRICH system in ePHENIX]] | ||
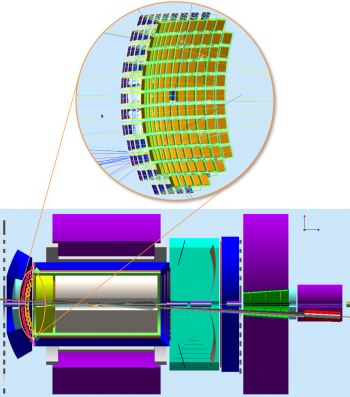
| + | *mRICH detector system in JLEIC. | ||
| + | *:[[image: MRICH in JLEIC.png |center|350px|mRICH in JLEIC]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Second mRICH Prototype Beam Test= | ||
| + | '''Technical Scope of Work (TSW)''' | ||
| + | *[[Media:T1048_FY2018_mRICH_v1.pdf | TSW document submitted to Fermilab]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:50, 1 June 2018
The goal of the modular aerogel RICH (mRICH) is to provide hadronic PID capability with momentum coverage from 3 to 10 GeV/c with a compact design in order to overcome the space limitations of the EIC experiments. Although the multi-layer proximity-focusing RICH design, such as ARICH at BELLE2, can achieve three-sigma K/π separation at 4 GeV/c, a larger expansion volume is required for PID in higher momentum range.
A multi-layer proximity-focusing RICH design increases PID separation power by increasing number of detected photons (Nγ) by adding successive layers of radiator while keeping the uncertainty of Cherenkov angle (σ_θ) of single photon measurement. In contrast, the novel lens-based mRICH design improves the separation power by minimizing the uncertainty σ_θ as a result of lens focusing, and requires a smaller coverage of the photosensor plane.
Contents
Detector Design
Modular RICH detector consist of a block of aerogel as a radiator, a Fresnel lens, a set of four-sided mirror, and a sensor plane. When charged particle passes through the aerogel, it will emit Cherenkov photons in a cone shape. These Cherenkov photons will be focused by the Fresnel lens on the sensor plane, and form a shape ring image.
| Figure 1.1 (a). Modular RICH detector in GEMC simulation | Figure 1.1 (b). Single 9 GeV/c pion simulation |
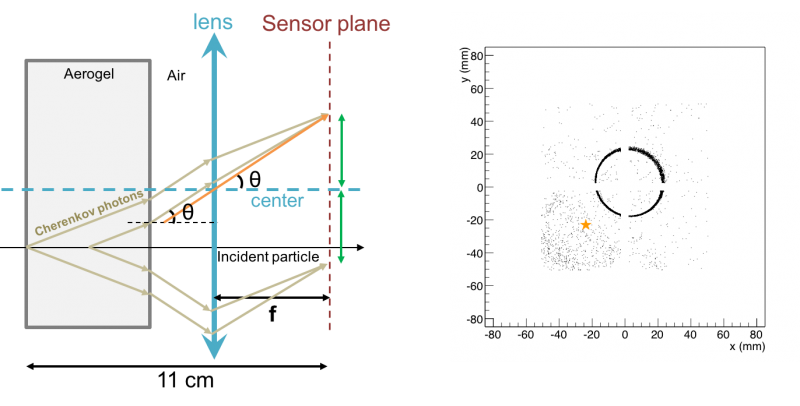
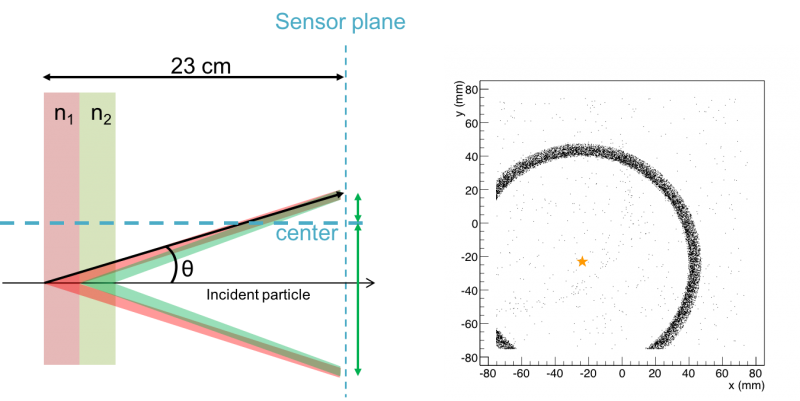
There are two advantages of the lens-based design. Firstly, the ring image is smaller and thinner because of the focusing of lens (see figure 1.2 and 1.3). Secondly, in the case that charged particle travelling parallel but off the longitudinal axis (that is, the optical principal of lens), ring image will be shifted to the central area of the sensor plane (see figure 1.4 and 1.5). Therefore, the lens-based design enhances detector PID performance, while lowers the required sensor plane area per ring.
| Figure 1.2. Lens focusing gives thinner Cherenkov ring image compare to BELLE-2 ARICH design (below) |
| Figure 1.3. BELL-2 ARICH design a double layer proximity focusing RICH detector. By using two different refractive indices aerogel block, in order to increase number of photons detected while keeping uncertainty of single photon measurement. |
| Figure 1.4. When the charge particle incident along the z-axis of the detector, Cherenkov ring image from the incident particle will be shifted to the central area of the sensor plane, resulting fewer photon loss, and reduce image distortion. |
| Figure 1.5. Cherenkov ring image from particles that are incident at the third quadrant of the detector. |
Fisrt Prototype and Beam Test
First Prototype
| Figure 2.1. First mRICH prototype |
| Component | Property |
|---|---|
| Detector holder box | acrylic |
| Aerogel | refractive index=1.03 |
| Fresnel lens | spheric acrylic Fresnel lens. focal length=3" |
| Mirror set | |
| Sensor | HAMAMATSU 8500 PMT array. Pixel size=6×6mm |
First Beam Test
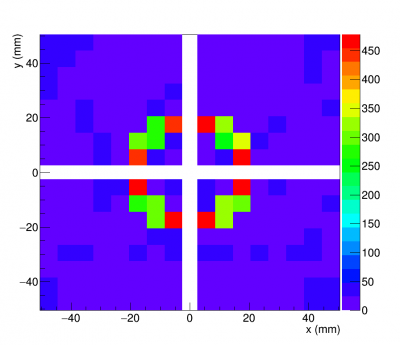
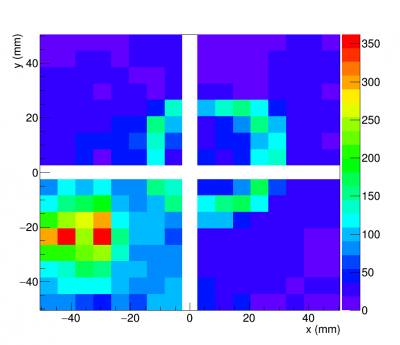
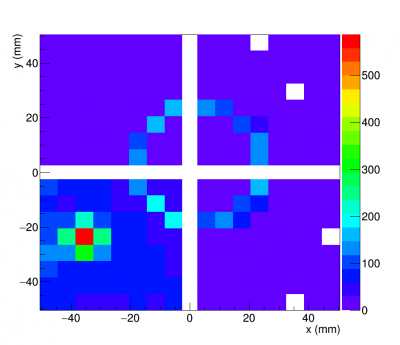
Beam test set up at Fermilab Test Beam Mtest Facility for the first modular RICH prototype detector is shown in the picture below. The detector (black box) sit at the center of a aluminium frame. On both ends of the aluminium frame are hodoscopes. Each hodoscopes consist of four horizon finger-size (1cm x 1cm) scintillators, and four vertical finger-size scintillators. On the far right of the aluminium frame was trigger paddle. The beam was coming from right to left of the picture.
| Figure 3.1. Beam test set up at Fermilab Test Beam Mtest Facility for the first modular RICH prototype detector. |
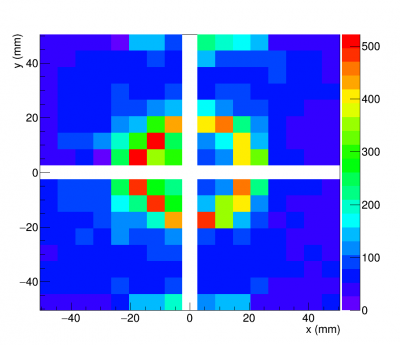
Accumulated hit maps from test beam data (right) and simulation (left) are shown in figure (3.2) and (3.3).
Second Prototype
Optimized Detector Design
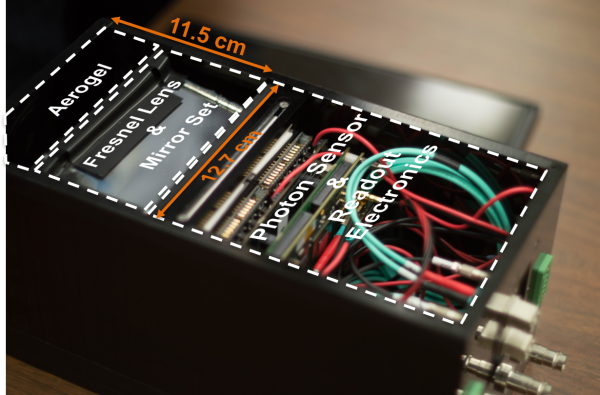
In order to enhance detector PID performance, the next mRICH prototype will use a longer focal length (6") Fresnel lens, and smaller pixel size (3mm × 3mm) photon sensors. Furthermore, the readout electronics will be separated from the optical components to avoid overheating.
|
| Figure 3.1. (left) 3D drawing of the second mRICH prototype. (right) construction of the second mRICH prototype. |
| Component | Property |
|---|---|
| Detector holder box | Aluminum |
| Aerogel | refractive index=1.03 |
| Fresnel lens | spheric acrylic Fresnel lens. focal length=6" |
| Mirror set | |
| Sensor | HAMAMATSU 13700 PMT array. Pixel size=3×3mm |
Projected Detector Performance of Next mRICH Prototype
mRICH Detector System Simulation
- mRICH detector system in sPHENIX/ePHENIX. The detector system which contains 284 modules of mRICH, covers 1.0 to 2.0 rapidity.
- Event display of 10 negative pion tracks (view from down stream) from simulation. An enlarged view is shown on the left.
- mRICH detector system in JLEIC.
Second mRICH Prototype Beam Test
Technical Scope of Work (TSW)